Direct biosensor detection of botulinum neurotoxin endopeptidase activity in sera from patients with type A botulism.
Résumé
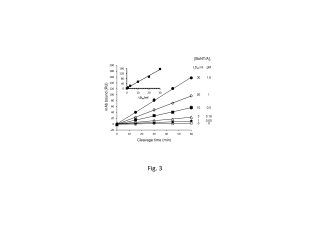
: Botulinum neurotoxin A (BoNT/A) has intrinsic endoprotease activity specific for SNAP-25, a key protein for presynaptic neurotransmitter release. The inactivation of SNAP-25 by BoNT/A underlies botulism, a rare but potentially fatal disease. There is a crucial need for a rapid and sensitive in vitro serological test for BoNT/A to replace the current in vivo mouse bioassay. Cleavage of SNAP-25 by BoNT/A generates neo-epitopes which can be detected by binding of a monoclonal antibody (mAb10F12) and thus measured by surface plasmon resonance (SPR). We have explored two SPR assay formats, with either mAb10F12 or His6-SNAP-25 coupled to the biosensor chip. When BoNT/A was incubated with SNAP-25 in solution and the reaction products were captured on a mAb-coated chip, a sensitivity of 5fM (0.1LD50/ml serum) was obtained. However, this configuration required prior immunoprecipitation of BoNT/A. A sensitivity of 0.5fM in 10% serum (0.1 LD50/ml serum) was attained when SNAP-25 was coupled directly to the chip, followed by sequential injection of BoNT/A samples and mAb10F12 into the flow system to achieve on-chip cleavage and detection, respectively. This latter format detected BoNT/A endoprotease activity in 50-100µl serum samples from all patients (11/11) with type A botulism within 5h. No false positives occurred in sera from healthy subjects or patients with other neurological diseases. The automated chip-based procedure has excellent specificity and sensitivity, with significant advantages over the mouse bioassay in terms of rapidity, required sample volume and animal ethics.
Fichier principal
 Figure_3_Leveque_et_al.pdf (33.35 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_1_Leveque_et_al.pdf (12.26 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_2_Leveque_et_al.pdf (162.88 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_4_Leveque_et_al.pdf (13.78 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_5_Leveque_et_al.pdf (21.91 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Leveque_et_al.pdf (315.97 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_3_Leveque_et_al.pdf (33.35 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_1_Leveque_et_al.pdf (12.26 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_2_Leveque_et_al.pdf (162.88 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_4_Leveque_et_al.pdf (13.78 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Figure_5_Leveque_et_al.pdf (21.91 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
Leveque_et_al.pdf (315.97 Ko)
Télécharger le fichier
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|
| Origine | Fichiers produits par l'(les) auteur(s) |
|---|